1.概述
list是一个很常用的数据结构。Redis中实现的list基于双向链表。该实现简单,高效。list是实现其他数据结构的基础结构。
2.实现
所在文件:adlist.h和adlist.c。
list数据结构如下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
// list节点结构
typedef struct listNode {
// 指向前一个节点,head的prev字段为NULL
struct listNode *prev;
// 指向后一个节点,tail的next字段为NULL
struct listNode *next;
// 值
void *value;
} listNode;
// list结构
typedef struct list {
// 头指针
listNode *head;
// 尾指针
listNode *tail;
// 用于复制值的函数指针
void *(*dup)(void *ptr);
// 用于释放值得函数指针
void (*free)(void *ptr);
// 用于比较匹配值的函数指针
void (*match)(void *ptr, void *key);
// list长度
unsigned long len;
} list;
|
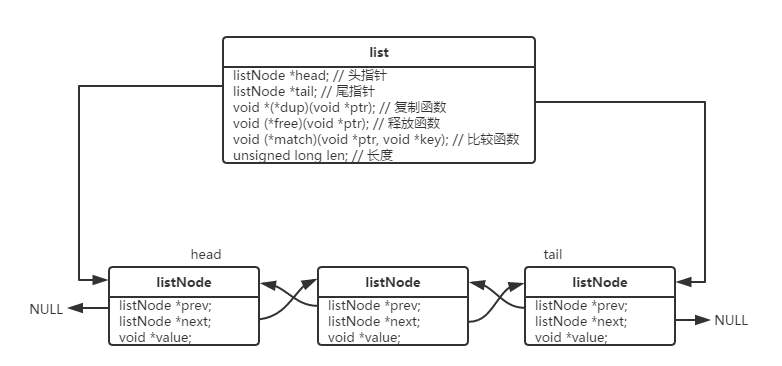
节点值存放在一个void *中,可以通过设置dup(复制)、free(释放)、match(匹配,比较)自定义对值的操作。
同时定义了一个迭代器结构用于遍历整个list,可以顺序或逆序遍历(以宏AL_START_HEAD和AL_START_TAIL表示)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
typedef struct listIter {
// 下个节点
listNode *next;
// 迭代方向
int direction;
} listIter;
|
3.操作
3.1.创建
listCreate创建一个新的list。出现错误时,返回NULL。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
list *listCreate(void)
{
struct list *list;
// 分配空间
if ((list = zmalloc(sizeof(*list))) == NULL)
return NULL;
// 所有字段设置为空
list->head = list->tail = NULL;
list->len = 0;
list->dup = NULL;
list->free = NULL;
list->match = NULL;
return list;
}
|
3.2.销毁
listRelease销毁这个list。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
void listRelease(list *list)
{
unsigned long len;
listNode *current, *next;
current = list->head;
while(len--) {
next = current->next;
// 如果自定义了free,使用该函数释放值
if (list->free) list->free(current->value);
zfree(current);
current = next;
}
zfree(list);
}
|
3.3.插入节点
通过下面几个函数实现在不同的位置插入新节点:
在头部插入
listAddNodeHead在头部插入一个节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
list *listAddNodeHead(list *list, void *value)
{
listNode *node;
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
node->value = value;
if (list->len == 0) {
// list为空
list->head = list->tail = node;
node->prev = node->next = NULL;
} else {
// 修改对应指针指向,让node成为head
node->prev = NULL;
node->next = list->head;
list->head->prev = node;
list->head = node;
}
list->len++;
return list;
}
|
在尾部插入
listAddNodeTail在尾部插入一个节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
list *listAddNodeTail(list *list, void *value)
{
listNode *node;
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
node->value = value;
if (list->len == 0) {
// list为空
list->head = list->tail = node;
node->prev = node->next = NULL;
} else {
// 修改对应指针指向,让node成为tail
node->prev = list->tail;
list->tail->next = node;
list->tail = node;
}
list->len++;
return list;
}
|
在指定节点前后插入
listInsertNode在指定节点处插入节点。after标志指示在节点前还是节点后插入。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
list *listInsertNode(list *list, listNode *old_node, void *value, int after) {
listNode *node;
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
node->value = value;
if (after) {
// 在old_node之后插入
node->prev = old_node;
node->next = old_node->next;
// 在尾部后插入,需要更新尾部
if (list->tail == old_node) {
list->tail = node;
}
} else {
// 在old_node之前插入
node->next = old_node;
node->prev = old_node->prev;
// 在头部前插入,需要更新头部
if (list->head == old_node) {
list->head = node;
}
}
// 修正node的前后节点的指向
if (node->prev != NULL) {
node->prev->next = node;
}
if (node->next != NULL) {
node->next->prev = node;
}
list->len++;
return list;
}
|
3.4.删除节点
listDelNode删除指定节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
void listDelNode(list *list, listNode *node)
{
// 不是头部
if (node->prev)
node->prev->next = node->next;
// 是头部,删除该节点需要修正head
else
list->head = node->next;
// 不是尾部
if (node->next)
node->next->prev = node->prev;
// 是尾部,删除该节点需要修正tail
else
list->tail = node->prev;
// 如果自定义free,使用该函数释放value
if (list->free) list->free(node->value);
zfree(node);
list->len--;
}
|
3.5.遍历
list提供遍历器,可以实现顺序或逆序遍历
获取迭代器
listGetIterator获取一个list的迭代器,方向由direction指定。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
listIter *listGetIterator(list *list, int direction)
{
listIter *iter;
if ((iter = zmalloc(sizeof(*iter))) == NULL) return NULL;
// 顺序
if (direction == AL_START_HEAD)
iter->next = list->head;
// 逆序
else
iter->next = list->tail;
iter->direction = direction;
return iter;
}
|
listGetIterator获取的迭代器需要调用listReleaseIterator释放。
1
2
3
|
void listReleaseIterator(listIter *iter) {
zfree(iter);
}
|
遍历
listNext返回迭代器的当前值,并将其后移一位指向下一个值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
listNode *listNext(listIter *iter)
{
listNode *current = iter->next;
if (current != NULL) {
// 顺序
if (iter->direction == AL_START_HEAD)
iter->next = current->next;
// 逆序
else
iter->next = current->prev;
}
return current;
}
|
重置迭代器
遍历结束之后,如果需要重新遍历。可以重置迭代器,不用创新创建。重置时可以选择从头部还是尾部开始遍历。
listRewind重置迭代器,可以重新顺序遍历。
1
2
3
4
|
void listRewind(list *list, listIter *li) {
li->next = list->head;
li->direction = AL_START_HEAD;
}
|
listRewindTail重置迭代器,可以重新逆序遍历。
1
2
3
4
|
void listRewindTail(list *list, listIter *li) {
li->next = list->tail;
li->direction = AL_START_TAIL;
}
|
3.6.其他操作
复制list
listDup复制当前list,返回一个新的list。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
list *listDup(list *orig)
{
list *copy;
listIter *iter;
listNode *node;
if ((copy = listCreate()) == NULL)
return NULL;
copy->dup = orig->dup;
copy->free = orig->free;
copy->match = orig->match;
iter = listGetIterator(orig, AL_START_HEAD);
while((node = listNext(iter)) != NULL) {
void *value;
if (copy->dup) {
// 如果自定义了dup,使用该函数复制值
value = copy->dup(node->value);
if (value == NULL) {
// 空间分配失败,清理,返回NULL
listRelease(copy);
listReleaseIterator(iter);
return NULL;
}
} else {
value = node->value;
}
if (listAddNodeTail(copy, value) == NULL) {
// 空间分配失败,清理,退出
listRelease(copy);
listReleaseIterator(iter);
return NULL;
}
}
listReleaseIterator(iter);
return copy;
}
|
查找指定key
listSearchKey遍历list查找指定的key。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
listNode *listSearchKey(list *list, void *key)
{
listIter *iter;
listNode *node;
iter = listGetIterator(list, AL_START_HEAD);
while((node = listNext(iter)) != NULL) {
if (list->match) {
// 如果自定义了match,使用该函数匹配比较
if (list->match(node->value, key)) {
listReleaseIterator(iter);
return node;
}
} else {
// 否则直接比较地址
if (key == node->value) {
listReleaseIterator(iter);
return node;
}
}
}
listReleaseIterator(iter);
return NULL;
}
|
返回指定索引处节点
listIndex返回指定索引处的节点,索引为负时从尾部计算。索引0表示第一个节点,1表示第二个节点,索引-1表示倒数第一个节点等等。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
listNode *listIndex(list *list, long index) {
listNode *n;
if (index < 0) {
// index < 0时从尾部计算
index = (-index)-1;
n = list->tail;
while(index-- && n) n = n->prev;
} else {
// index >= 0时从头部计算
n = list->head;
while(index-- && n) n = n->next;
}
}
|
将最后一个节点移到头部
listRotate将最后一个节点移到头部。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
void listRotate(list *list) {
listNode *tail = list->tail;
if (listLength(list) <= 1) return;
// 分离尾节点
list->tail = tail->prev;
list->tail->next = NULL;
// 移到头部
list->head->prev = tail;
tail->next = list->head;
list->head = tail;
}
|
4.总结
C语言缺乏基本的数据结构,在用到指定数据结构时,要么使用第三方实现,要么自己实现。
