1.概述
dict是Redis中最重要的数据结构之一。很多结构都使用dict作为基础数据结构,例如hash类型,命令表,SHA1到Lua脚本的映射等。
2.实现结构
dictEntry表示为一个哈希表节点。key使用一个void *类型来表示,value由几个常见类型的union来表示。由于使用链地址法,所以dictEntry中存放了下一个节点的地址next。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key;
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;
|
dictType表示一个dict的相关方法,类似于C++中的类方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
typedef struct dictType {
// hash函数,为key生成hash
unsigned int (*hasFunction)(const void *key);
// key复制函数
void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);
// value复制函数
void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);
// key比较函数
int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);
// key销毁函数
void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);
// value销毁函数
void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
} dictType;
|
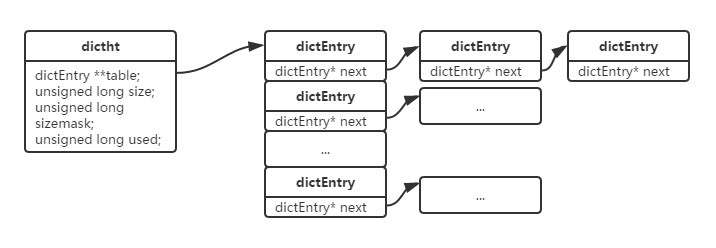
dictht是一个链地址法哈希表。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
typedef struct dictht {
// 哈希表的槽
dictEntry **table;
// 哈希表槽个数,是2的整数次幂
unsigned long size;
// size-1,计算出一个key的hash后,直接 hash & sizemask即可算出所属的槽
unsigned long sizemask;
// 已使用大小
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
|
dict是字典类型,包含两个dictht以实现增量rehash。增量rehash可以避免一次rehash耗费时间过长,导致其他操作阻塞的情形。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
// 每个dict可以额外关联一些数据
void *privdata;
// 两个dictht,方便实现增量rehash
dictht ht[2];
// rehashidx表示rehash索引,不在rehash时,该字段为-1
long rehashidx;
// 该dict生成的安全迭代器的数量,有安全迭代器时不能rehash
int iterators;
} dict;
|
另外定义了遍历一个dict的迭代器。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
typedef struct dictIterator {
dict *d;
// 槽索引
long index;
// table为dictht索引只能为0或1,safe表示是否需要安全的遍历(遍历过程中不能rehash)
int table, safe;
// 当前entry和下一个entry
dictEntry *entry, *nextEntry;
// 表示当前状态的一个64位整数,非安全迭代器初始化时计算这个值
// 释放迭代器时再次计算并比较两个值,如果不同说明用户在迭代过程中执行了非法操作
long long fingerprint;
} dictIterator;
|
定义文件:dict.h和dict.c。
3.dict操作
3.1.创建dict
调用dictCreate先分配空间。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
// 参数type自定义对哈希表节点的key和value进行的操作
// 参数privDataPtr可以存放用户自定义信息,在type的操作函数中可以取得这个值
dict *dictCreate(dictType *type, void *privDataPtr)
{
// 分配空间
dict *d = malloc(sizeof(*d));
// 初始化
_dictInit(d,type,privDataPtr);
return d;
}
|
然后调用_dictInit初始化各字段。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
int _dictInit(dict *d, dictType *type, void *privDataPtr)
{
// 重置dictht内容
_dictReset(&d->ht[0]);
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
d->type = type; // 设置操作
d->privdata = privDataPtr; // 自定义信息
d->rehashidx = -1; // 不在rehash中
d->iterators = 0; // 生成的安全迭代器数量为0
return DICK_OK;
}
|
_dictInit会调用_dictReset重置两个dictht内容。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
static void _dictReset(dictht *ht)
{
ht->table = NULL; // 初始化槽为空
ht->size = 0; // 初始化槽大小为0
ht->sizemask = 0;
ht->used = 0; // 没有元素
}
|
3.2.添加节点
调用dictAdd添加节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
int dictAdd(dict *d, void *key, void *val)
{
// dictAddRaw会新建一个entry,插入对应的位置。同时还会处理rehash的情况。
dictEntry *entry = dictAddRaw(d,key);
// key已存在
if (!entry) return DICT_ERR;
// 定义在dict.h中的宏,设置value值
dictSetVal(d, entry, val);
return DICT_OK;
}
|
dictAddRaw创建新的节点,插入相应位置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
// 该函数插入entry,但是并不设置值。它返回entry,让调用者可以使用dictSet*Val系列函数设置值。
// 例如:
// entry = dictAddRaw(dict, mykey);
// if (entry != NULL) dictSetSignedIntegerVal(entry, 1000);
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key)
{
int index;
dictEntry *entry;
dictht *ht;
// 如果正在rehash,让其向前推进一步
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
// 返回一个槽,可以在其中插入一个entry
if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(d, key)) == -1)
return NULL;
// 如果在rehash,新key应该插入到新dictht中(即索引为1的dictht)
ht = dictIsRehashing(d) ? &d->ht[1] : &d->ht[0];
entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry));
entry->next = ht->table[index];
ht->used++;
dictSetKey(d, entry, key);
return entry;
}
|
3.3.查找节点
查找由函数dictFind负责,该函数实现也很简单。先计算key的hash值,找到对应的槽,依次比较。但是由于存在rehash状态,所以需要查找两个dictht。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
dictEntry *dictFind(dict *d, const void *key)
{
dictEntry *he;
unsigned int h, idx, table;
// 没有元素
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return NULL;
// 如果正在rehash,将其向前推进一步
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
// 计算hash值
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
// 计算槽索引
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
while (he) {
// 比较key,如果自定义了keyCompare,调用此函数比较,否则比较地址。
if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key))
return he;
he = he->next;
}
// 非rehash中,不用处理新dictht
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return NULL;
}
}
|
另外有个函数dictFetchValue可以取出entry的值。它直接使用dictFind完成其功能。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
void *dictFetchValue(dict *d, const void *key) {
dictEntry *he;
he = dictFind(d, key);
return he ? dictGetVal(he) : NULL;
}
|
3.4.随机一个节点
dictGetRandomKey随机返回一个dict中的entry。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
dictEntry *dictGetRandomKey(dict *d) {
dictEntry *he, *orighe;
unsigned int h;
int listlen, listele;
if (dictSize(d) == 0) return NULL;
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) {
// 在rehash中,需要在两个dictht中随机槽索引
do {
h = random() % (d->ht[0].size+d->ht[1].size);
he = (h >= d->ht[0].size) ? d->ht[1].table[h - d->ht[0].size] :
d->ht[0].table[h];
} while(he == NULL);
} else {
do {
h = random() & d->ht[0].sizemask;
he = d->ht[0].table[h];
} while (he == NULL);
}
// 链表长度
listlen = 0;
orighe = he;
while(he) {
he = he->next;
listlen++;
}
// 在链表中随机entry
listele = random() % listlen;
he = orighe;
while(listele--) he = he->next;
return he;
}
|
注意:
这个函数先随机槽,再随机链表元素,并不是等概率的。
3.5.设置节点
可以通过调用dictReplace设置一个key对应的value值。如果key不存在,则新增这个键值对。返回1表示新增,返回0表示更新值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
int dictReplace(dict *d, void *key, void *val) {
dictEntry *entry, auxentry;
// 先尝试新增。成功说明key不存在,已新增成功,直接返回。
if (dictAdd(d, key, val) == DICT_OK)
return 1;
// 查找key对应entry
entry = dictFind(d, key);
// 记录旧的entry,设置之后老的value需要释放!
auxentry = *entry;
dictSetVal(d, entry, val);
dictFreeVal(d, &auxentry);
return 0;
}
|
函数dictReplaceRaw进行以下处理:
- 如果key存在,返回key对应的entry
- 反之,插入这个key,然后返回新插入的entry
3.6.删除节点
节点删除通过dictGenericDelete完成,可以通过nofree指定是否销毁键和值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
static int dictGenericDelete(dict *d, const void *key, int nofree)
{
unsigned int h, idx;
dictEntry *he, *prevHe;
int table;
// 大小为0,删除失败
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return DICT_ERR;
// 如果正在rehash,将其向前推进一步
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
// 生成key的hash值
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
// 因为存在rehash状态,所以必须查找两个dictht
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
prevHe = NULL;
while(he) {
// 比较key
if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)) {
// 调整删除节点的前一个节点的next指向,如果为第一个节点调整table[idx]
if (prevHe)
prevHe->next = he->next;
else
d->ht[table].table[idx] = he->next;
if (!nofree) {
// 销毁键和值
dictFreeKey(d, he);
dictFreeVal(d, he);
}
zfree(he);
d->ht[table].used--;
return DICT_OK;
}
prevHe = he;
he = he->next;
}
// 如果没有在rehash,就不用遍历索引为1的dictht了
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break;
}
return DICT_ERR;
}
|
3.7.销毁dict
可以通过调用dictRelease删除一个dict。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
void dictRelease(dict *d)
{
// 清空两个dictht
_dictClear(d,&d->ht[0],NULL);
_dictClear(d,&d->ht[1],NULL);
zfree(d);
}
|
_dictClear负责清空dictht,释放所占空间。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
int _dictClear(dict *d, dictht *ht, void (callback)(void *)) {
unsigned long i;
for (i = 0; i < ht->size && ht->used > 0; i++) {
dictEntry *he, *nextHe;
if (callback && (i & 65535) == 0) callback(d->privdata);
if ((he = ht->table[i]) == NULL) continue;
while (he) {
nextHe = he->next;
// 释放键值
dictFreeKey(d, he);
dictFreeVal(d, he);
zfree(he);
ht->used--;
he = nextHe;
}
}
zfree(ht->table);
// 重置,后续可以再次使用
_dictReset(ht);
return DICT_OK;
}
|
3.8.清空dict
可以调用dictEmpty清空一个dict,但不销毁。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
void dictEmpty(dict *d, void(callback)(void*)) {
// 清空两个dictht
_dictClear(d,&d->ht[0],callback);
_dictClear(d,&d->ht[1],callback);
d->rehashidx = -1;
d->iterators = 0;
}
|
3.9.遍历dict
为了便于dict的遍历,Redis提供了dict的迭代器dictIterator。
迭代器分为安全的和非安全的两种,分别通过dictGetIterator和dictGetSafeIterator获取。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
dictIterator *dictGetIterator(dict *d)
{
dictIterator *d = zmalloc(sizeof(*iter));
iter->d = d;
iter->table = 0;
iter->index = -1;
iter->safe = 0;
iter->entry = NULL;
iter->nextEntry = NULL;
return iter;
}
dictIterator *dictGetSafeIterator(dict *d) {
dictIterator *i = dictGetIterator(d);
// 创建时不需要增加dict.iterators的值,在遍历正在开始后增加
i->safe = 1;
return i;
}
|
两种迭代器的区别:
通过dictNext获取迭代器的下一个值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
dictEntry *dictNext(dictIterator *iter)
{
while(1) {
if (iter->entry == NULL) {
dictht *ht = &iter->d->ht[iter->table];
// 遍历第一个元素时,安全迭代器需要增加dict.iterators值
// 非安全迭代器计算fingerprint
if (iter->index == -1 && iter->table == 0) {
if (iter->safe)
iter->d->iterators++;
else
iter->fingerprint = dictFingerprint(iter->d);
}
iter->index++;
// 一个dictht遍历完成,如果是索引为0,并且正在rehash,索引为1也可能有值,继续遍历。
// 否则直接break
if (iter->index >= (long)ht->size) {
if (dictIsRehashing(iter->d) && iter->table == 0) {
iter->table++;
iter->index = 0;
ht = &iter->d->ht[1];
} else {
break;
}
}
iter->entry = ht->table[iter->index];
} else {
iter->entry = iter->nextEntry;
}
if (iter->entry) {
iter->nextEntry = iter->entry->next;
return iter->entry;
}
}
return NULL;
}
|
遍历完成之后,调用dictReleaseIterator销毁迭代器。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
void dictReleaseIterator(dictIterator *iter) {
if (!(iter->index == -1 && iter->table == 0)) {
// 进行过遍历,释放时
// 安全迭代器需要减少dict.iterators值
// 非安全迭代器比较遍历前后fingerprint值
if (iter->safe)
iter->d->iterators--;
else
assert(iter->fingerprint == dictFingerprint(iter->d));
}
zfree(iter);
}
|
3.10.rehash
在上面添加key时,会调用_dictKeyIndex为key分配一个槽。_dictKeyIndex会调用_dictExpandIfNeeded,按需扩容。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d) {
// 正在rehash,不用处理
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_OK;
// 如果ht[0]大小为0,容量扩大为DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE。
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return dictExpand(d, DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE);
// 如果节点数量超过槽数量并且当前数量与总容量比大于dict_force_resize_ratio,扩容为当前数量的两倍。
// 如果设置了dict_can_resize,不需要判断比值
if (d->ht[0].used >= d->ht[0].size &&
(dict_can_resize ||
d->ht[0].used/d->ht[0].size > dict_force_resize_ratio))
{
return dictExpand(d, h->ht[0].used * 2);
}
}
|
dictExpand进行真正的扩容操作。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
int dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size) {
dictht n;
// 保证容量一定是2的整数次幂
unsigned long realsize = _dictNextPower(size);
// 正在rehash,不能扩容。
// 当前元素数量已经超过size了,肯定哪里出了问题
if (dictIsRehashing(d) || d->ht[0].used > size)
return DICT_ERR;
n.size = realsize;
n.sizemask = realsize-1;
n.table = zcalloc(realsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));
n.used = 0;
// 还没有元素,d->ht[0]设置为n即可
if (d->ht[0].table == NULL) {
d->ht[0] = n;
return DICT_OK;
}
// d->ht[1]设置为n,开始rehash
d->ht[1] = n;
// rehashidx=0表示正在rehash中,以后的新增都在新的dictht中操作
d->rehashidx = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
|
这条执行路径dictAddRaw -> _dictKeyIndex -> _dictExpandIfNeeded -> _dictExpand,没有显式进行rehash。后续进行其他操作时,会适当的时候调用_dictRehashStep。
1
2
3
4
|
static void _dictRehashStep(dict *d) {
// 没有生产迭代器时才能rehash
if (d->iterators == 0) dictRehash(d,1);
}
|
_dictRehashStep调用dictRehash处理:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;
// 执行n趟,每趟处理一个槽
while(n--) {
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
// 第一个dictht已经没有元素了,rehash完成!
// 将第二个dictht复制给第一个,重置第二个dictht,保证非rehash时,元素只在第一个dictht中
if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {
zfree(d->ht[0].table);
d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
d->rehashidx = -1;
return 0;
}
assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx);
while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) d->rehashidx++;
de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];
while(de) {
unsigned int h;
nextde = de->next;
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;
de->next = d->ht[1].table[h];
d->ht[1].table[h] = de;
d->ht[0].used--;
d->ht[1].used++;
de = nextde;
}
d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;
d->rehashidx++;
}
return 1;
}
|
dictRehashMilliseconds可以指定超时时间,rehash处理用时超过这个时间,就返回。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
int dictRehashMilliseconds(dict *d, int ms) {
long long start = timeInMilliseconds();
int rehashes = 0;
while (dictRehash(d, 100)) {
rehashes += 100;
// 超时了,break
if (timeInMilliseconds()-start > ms) break;
}
return rehashes;
}
|
函数dictResize将dict的大小指定为能容纳所有元素的最小值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
int dictResize(dict *d) {
int minimal;
if (!dict_can_resize || dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_ERR;
minimal = d->ht[0].used;
if (minimal < DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE)
minimal = DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE;
return dictExpand(d, minimal);
}
|
4.hash算法
5.dictType示例
dict.c最后列举了一个string copy的dictType示例。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
|
// 计算hash值
static unsigned int _dictStringCopyHTHashFunction(const void *key) {
return dictGenHashFunction(key, strlen(key));
}
static void *_dictStringDup(void *privdata, const void *key) {
int len = strlen(key);
// 重新copy一份string
char *copy = zmalloc(len+1);
// 防止编译器“未使用变量”警告
DICT_NOTUSED(privdata);
memcpy(copy, key, len);
copy[len] = '\0';
return copy;
}
static int _dictStringCopyHTKeyCompare(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2) {
DICT_NOTUSED(privdata);
// 使用c str的比较方式
return strcmp(key1, key2) == 0;
}
// 销毁key
static void _dictStringDestructor(void *privdata, void *key) {
DICT_NOTUSED(privdata);
zfree(key);
}
// 只为key重新分配空间,value共享指针
dictType dictTypeHeapStringCopyKey = {
_dictStringCopyHTHashFunction, // hash计算函数
_dictStringDup, // key复制函数,重新分配空间,复制
NULL, // value复制函数,为NULL,直接指针赋值
_dictStringCopyHTKeyCompare, // key比较函数,使用c str比较方式
_dictStringDestructor, // key销毁函数,因为是重新分配空间,所以需要显示free
NULL, // value销毁函数,value是共享指针,不定义销毁函数
};
// key和value都不重新分配空间,只共享指针
dictType dictTypeHeapStrings {
_dictStringCopyHTHashFunction, // hash计算函数
NULL, // key复制函数,为NULL,直接指针赋值
NULL, // value复制函数,为NULL,直接指针赋值
_dictStringCopyKeyHTKeyCompare, // key比较函数,使用c str比较方式
_dictStringDestructor, // key销毁函数
NULL, // value销毁函数
};
// key和value都重新分配空间
dictType dictTypeHeadStringCopyKeyValue = {
_dictStringCopyHTHashFunction, // hash计算函数
_dictStringDup, // key复制函数,重新分配空间,复制
_dictStringDup, // value复制函数,重新分配空间,复制
_dictStringCopyHTKeyCompare, // key比较函数,使用c str比较方式
_dictStringDestructor, // key销毁函数,因为是重新分配空间,所以需要显示free
_dictStringDestructor, // value销毁函数,因为是重新分配空间,所以需要显示free
};
|
